Qinsun Instruments Co.,Ltd
Contact:qinsun
TEL:+86 132 6275 2056
Email:sales@moutainchem.com
Fax:+86 132 6275 2056
Address:No.258 Ban Ting road, Song Jiang district, Shanghai
Next-Generation Rolling-Up Machines: Integration of AI, IoT, and Advanced Materials
2025-04-07
1. AI-Driven Process Optimization
Modern rolling-up machines now incorporate AI algorithms to enhance real-time decision-making and process autonomy. Key developments include:
- Predictive Maintenance: Machine learning models analyze vibration, temperature, and acoustic data to predict component failures before they occur. For example, General Electric’s Predix platform reduces unplanned downtime by 35% in steel rolling mills.
- Adaptive Control Systems: Neural networks dynamically adjust roll gaps, rolling speeds, and lubrication based on material properties. A 2023 study showed that AI-controlled systems improved thickness uniformity in aluminum foil production from ±3% to ±0.5%.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical machines simulate process variables (e.g., stress distribution, thermal gradients), enabling pre-production optimization and reducing trial-and-error testing.
2. IoT-Enabled Smart Factories
The integration of IoT sensors and cloud computing has birthed "smart" rolling-up machines capable of seamless communication across production lines:
- Real-Time Data Analytics: Sensors monitor parameters like roll torque, material flow rate, and energy consumption, transmitting data to centralized dashboards for analysis. Bosch’s IoT-enabled rolling systems achieve 20% energy savings through dynamic load balancing.
- Remote Diagnostics: Operators access machine health metrics globally via cloud platforms, enabling rapid troubleshooting. For instance, Siemens’ MindSphere ecosystem reduced service response times by 50% in automotive manufacturing.
- Interoperability: Standardized protocols (e.g., OPC UA) allow rolling-up machines to synchronize with ancillary systems like CNC laser cutters and robotic arms, streamlining end-to-end workflows.
3. Advanced Material Innovations
Emerging materials demand specialized rolling-up technologies tailored to extreme properties:
- High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs): Rolling machines with nanostructured rolls and ultra-precise temperature controls process HEAs for aerospace components resistant to oxidation and fatigue.
- Graphene-Reinforced Composites: Cold rolling techniques integrate graphene layers into polymers, enhancing strength and thermal conductivity for electronics applications.
- Shape-Memory Alloys (SMAs): Custom rolling-up processes exploit SMA’s self-healing properties to create durable medical stents and aerospace actuators.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
The industry is prioritizing eco-friendly practices to meet global decarbonization goals:
- Regenerative Braking Systems: Capturing kinetic energy during deceleration reduces power consumption by up to 25% in heavy-duty rolling operations.
- Closed-Loop Lubrication: AI-managed systems recycle lubricants, cutting waste by 40% while maintaining friction coefficients below 0.05.
- Lightweight Design: Hollow rolls made from titanium alloys reduce energy use without compromising structural integrity.
5. Industry-Specific Applications
a. Automotive Manufacturing
- Battery Foil Production: Ultra-thin copper and aluminum foils (<10 μm) rolled for EV batteries require nanosecond-level process control to prevent micro-pitting.
- Hydroforming Integration: Hybrid rolling-hydroforming machines create complex automotive chassis parts with 60% material savings.
b. Electronics
- Flexible PCBs: Roll-to-roll (R2R) electroplating systems enable mass production of wearable electronics with sub-10 μm trace resolution.
- OLED Screening: Precision rolling aligns organic light-emitting diode materials at molecular levels, achieving 99.9% pixel uniformity.
c. Defense and Aerospace
- Hypersonic Material Processing: Rolling-up machines equipped with plasma-assisted heating systems treat titanium alloys to withstand Mach 5+ temperatures.
- Stealth Coating Applications: Multi-axis rolling deposits radar-absorbing materials with 0.1° angular precision for aircraft stealth panels.
6. Challenges and Future Roadmaps
While progress is rapid, challenges persist:
- Material Waste: Achieving zero-defect rolling remains elusive. AI-guided predictive models aim to reduce scrap rates to <1%.
- Skill Gaps: Upskilling technicians in AI and IoT management is critical. Companies like Fanuc now offer "smart technician" certification programs.
- Standardization: The lack of global standards for IoT interoperability hinders scalability. Initiatives like ISO 22436 (Industrial IoT) aim to resolve this.
Future R&D focuses on quantum computing-powered optimization, self-healing materials, and fully autonomous rolling-up factories where AI orchestrates every process parameter.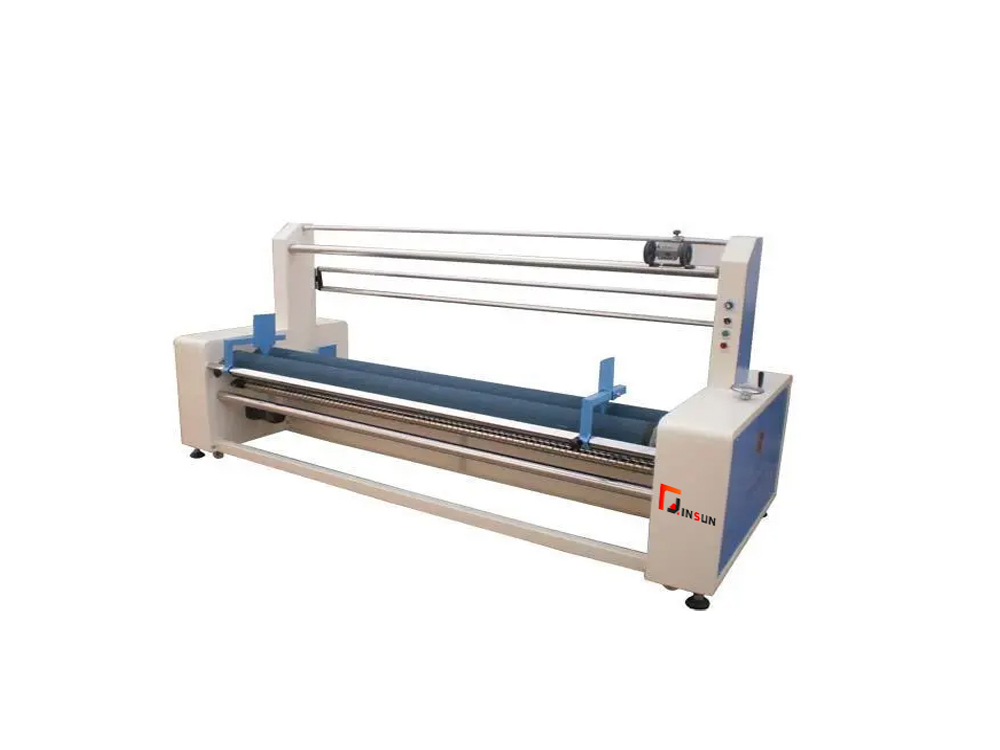
Previous post:Operating specification for optical rotation analyzers
Next chapter:Air Flow Resistance Tester: Principles, Applications, and Technological Advancements
PRODUCT
-
Anodized Powder Coating

-
Standard Building Materials Powder Coating

-
Powder Coating For Curtain Wall

-
CAR WHEELS ARE MADE OF POWDER

-
Antimicrobial Powder Coatings

-
GENERAL INDUSTRIAL POWDER

-
Bicycle Powder Coating-Durable Powder Coating for Frames

-
Rim Powder Coating

-
Electrical Appliance Powder Coating

-
Road Barrier Powder Coating

NEWS
- Tianjin Chenxi Garden Powder Coating: Application Adaptation Guide for Beautiful, Durable Spaces 2025-12
- Transparent Powder Coating: Reveal Texture, Guard Durability 2025-12
- Standard International Group (HK) Limited Partners With Artisanal Textile Coatings Lisboa – Redefini 2025-12
- Artistic Powder Coatings: Where Creativity Meets Industrial Durability 2025-12
- Anti-Corrosion Powder Coatings for Pipelines 2025-12
- Iberian Surface Solutions SL Partners And Matte Powder Coating 2025-12
- Analyzing Functional Problems Encountered in Powder Coating Production and Spraying 2025-12
- A Brief Discussion on Powder Coatings and Surface Tension 2025-12
- What is Fluorocarbon Coating in Aluminum Profile Processing? 2025-12
- Electrical Appliance Powder Coating: From Traditional Craftsmanship to a Green Future 2025-12





 TEL:+86 132 6275 2056 Copyright © 2021-2024 Shanghai Qinsun Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. qinsun
TEL:+86 132 6275 2056 Copyright © 2021-2024 Shanghai Qinsun Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. qinsun
 Address:No.258 Ban Ting road, Song Jiang district, Shanghai
Address:No.258 Ban Ting road, Song Jiang district, Shanghai
